Section 1.3 explains the different types of transformations in graphs.
The first type is a translation- a shift in the graph (left/right or up/down)
When adding or subtracting from y, the graph moves up or down, for example,
When adding or subtracting from x, the graph moves left or right, for example,
The graph moves to the right when c is negative.
The graph would move to the left if c were positive.
The second type is a dilation- a change in the shape of the graph
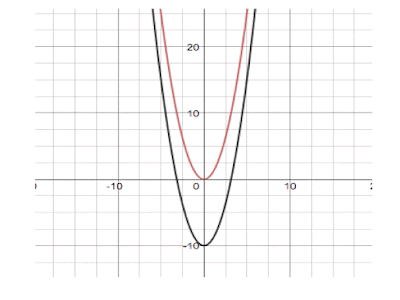
To vertically shrink the graph, multiply y by a number less than one but greater than zero.
To vertically stretch the graph, multiply y by a number greater than one.
To horizontally shrink the graph, multiply x by a number greater than one. The opposite is true to stretch the graph, multiply x by a number less than one but greater than zero. For example,
The third type is a reflection- a change about the x or y axis
To reflect upon the x-axis, multiply the y values by -1
To reflect upon the y-axis, multiply the x value by -1




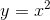





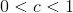











No comments:
Post a Comment