For
One-to-One Properties:
ex: 
2).  if and only if
if and only if 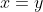
ex:
Inverse Properties:
1). 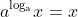
ex:
2). 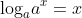
ex:
The examples above are the very basic to clearly show how the one-to-one and inverse properties can be used to solve logarithmic and exponential equations. The strategies to solve logarithmic and exponential equations can be summarized through the following:
- Rewrite the given equation in a form to use the One-to-One properties of exponential or logarithmic functions.
- Rewrite an exponential equation in logarithmic form and apply the inverse property of logarithmic functions.
- Rewrite a logarithmic equation in exponential form and apply the Inverse property of exponential functions.
Change-of-Base formula
The Change-of-Base formula shows that: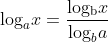
This is proved through the following:
let 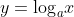
Solving Exponential Equations
Algebraic Solution:
Solve: 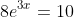
Graphical Solution:
Enter  and
and  into your calculator
into your calculator
use the intersect or zoom and trace features to approximate the intersection point. This graph shows that the two equations intersect at (0.074,10) or 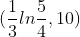
Graphical Solution 2:
rewrite the original equation as 
Use the zero root feature or the zoom and trace features to approximate the x-intercept(s). the zero on this graph is shown at (0.074,0) or 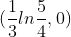
Solving an Exponential Equation in Quadratic Form:
Algebraic solution:
Solve: 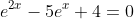
*Check both of these solutions in the original equation to see if either is extraneous*
To find the solutions to this equation graphically, use the second graphical solution method shown above.
Solving Logarithmic Equation
 subtract 6 from each side
subtract 6 from each side
 divide each side by 2
divide each side by 2
 exponentiate each side
exponentiate each side
 Inverse property to solve
Inverse property to solve

Algebraic Solution:
Solve: 
Graphical Solution:
Enter  and
and  into your graphing utility
into your graphing utility
use the intersect or zoom and trace features to approximate the intersection point. This graph shows that the two equations intersect at (0.707, 5). 0.707=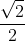
Checking for Extraneous Solutions:
Algebraic Equation:
solve: 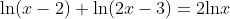
By checking both of the solutions with the original equation, we can conclude that x=1 is an extraneous answer. This is because the solution x=1 creates the equation  , and -1 is outside of the domain of a natural log function.
, and -1 is outside of the domain of a natural log function.
Graphical Solution:
Rewrite the original equation as 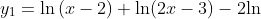
Use the zero root feature or the zoom and trace features to approximate the x-intercept(s). the zero on this graph is shown at (6,0).
 rewrite
rewrite
 graph
graph
Approximating Solutions
This method should be utilized for equations that contain combinations of algebraic functions, exponential functions, and/or logarithmic functions that will be messy by solving algebraically.
example:
solve: 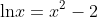
We can approximate the two solutions of this equation to be 0.138 and 1.56. After, Check solutions with original equation.





No comments:
Post a Comment